EXO-CD24
The new generation of immunomodulators, better than steroids
Our approach
EXO-CD24 is the next generation of immunomodulators, offering a better, safer and smarter alternative to steroids and other immunomodulators. This precision nanotechnology is designed to target the cytokine storm, the main complication in a wide range of pulmonary and systemic diseases. EXO-CD24 combines two groundbreaking technologies: exosomes (the carriers) engineered to overexpress CD24 (the drug), a novel innate checkpoint protein.

Exosomes
advanced therapy, a promising and relatively new therapeutic area. The exosomes are nano-sized lipid vesicles secreted by most cell types, normal and diseased, and transmit information to other cells via delivery of biologically active cargo.
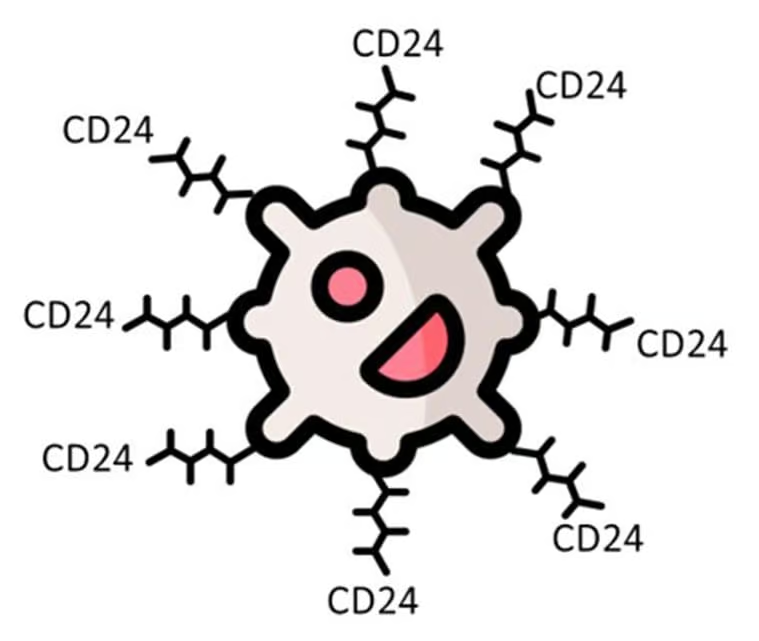

CD24
a small, heavily-glycosylated glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein that, among other things, functions as a cell adhesion molecule, an immune checkpoint, and a biological immunomodulator.
Administration by Inhalation is a significant clinical advantage: it is simple, non-invasive and does not require any professional medical team
EXO-CD24 is administered by inhalation directly into the lungs to suppress the inflammatory response to tissue injuries. The potential efficacy stems from using an endogenous immunomodulator of the immune system (CD24). Safety has been secured by using natural exosomes, promising endogenous drug carriers, hence they do not trigger immune responses, the main cause of side effects.
EXO-CD24 safety and promising efficacy were confirmed in-vitro, in-vivo and in humans.
The drug can be given everywhere, by anyone- even by the patient himself
Technological innovation

Mechanism of Action (MOA)
EXO-CD24 is the first-in class technology allowing the immune system to distinguish between self, Damage Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs), released from damaged or dying cells, and non-self, Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs), derived from pathogens like bacteria, parasites and viruses. While CD24 suppresses immune activation triggered by DAMPs, it does not interfere with the immune system's recognition of PAMPs.
CD24 also attenuates NFĸB activation, thereby reducing overall immune activation.
The unique MOA of EXO-CD24 ensures that its therapeutic efficacy is not dependent on factors like viral variants or disease severity, offering a platform to treat a variety of medical conditions.
Clinical data - efficacy without toxicity in >250 ARDS patients with 4Y of follow-up`
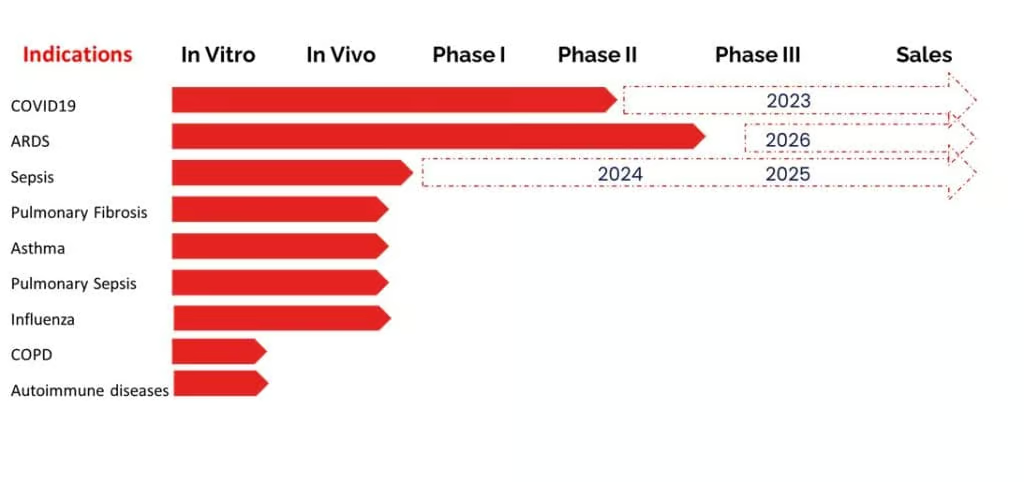
EXO-CD24 can treat various indications, with its primary POC use in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
A Phase Ib/IIa open-label study was conducted in Tel-Aviv Medical Center (Israel), involving 35 participants who received escalating doses of aerosolized EXO-CD24 (ranging from 1x10⁸ to 1x10¹⁰ particles). Phase IIb study was a multi-center, single-blind, dose-finding trial conducted at three medical centers in Athens (Greece). This study confirmed EXO-CD24's high safety profile and promising efficacy of the drug. EXO-CD24 was also given to 15 severe ill ARDS patients who did not meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The ongoing Phase IIb study is a double-blind trial comparing EXO-CD24 to a placebo, taking place in Israel.
The pivotal study, pending on FDA/EMA approval will be conducted in over 20 leading medical centers across Europe, Israel and the US.
So far, over 250 ARDS patients have been treated with EXO-CD24 as part of clinical trials. The safety profile is exceptional, no serious adverse events (SAEs) or even adverse events (AEs) related to the drug, have been reported along with more than 4 years of follow-up and highly promising clinical and laboratory efficacy.
Beyond respiratory diseases, EXO-CD24 has potential as a treatment for a wide range of systemic diseases by suppressing inflammation. These include autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and graft-versus-host disease, among others. There is a significant and critical need for therapies to address severe cases of these diseases, to prevent long-term hospitalization, the need for ventilation, and death.

EXO-CD24 development pipeline